Forming Processes and Methods of Tees
Posted: 07/26/2022 08:51:27 Hits: 18
From the forming process, the tee can be roughly divided into three stages: (1) Filling stages: the pipe is put into the mold cavity, then the mold is closed; the pipe is injected with liquids, and the gas is removed. The two ends of the pipe are pressed with a horizontal punch at the same time. (2) Forming stages: the liquid of the pipe is continuously pressurized, and the punches at both ends of the pipe are fed to the middle according to the loading curve to supplement the material. Under the combined action of the internal pressure and the axial feed, the pipe is roughly formed. (3) Shaping stages: the pressure is gradually increased, so that the pipe and the transition fillet of the cavity are completely fitted and formed the target part. The feeding at this stage is very small. Observed from the radial section, the pipe can be formed with rectangular, trapezoid, oval or other profiled sections.
After decades of technological development, some experts and scholars at home and abroad have slightly improved the forming of tees, for example, pipe fittings formed by high pressure in a hot state. First, heat the mold to the specified temperature, then put the tube blank in the cavity to preheat; inject the hot medium into the pipe. When the pipe reaches the set temperature, start to apply pressure and axial feed to form the tube close to the inner cavity of the mold, forming a hollow variable cross-section part. Jianchun He and Xiaoting Xiao and others from the Guangdong University of Technology used the ABAQUS explicit algorithm to simulate the tee, and used the influence of the axial displacement variable and internal pressure variable on the height, maximum and minimum wall thickness of the formed branch pipe, and analyzed the distribution of wall thickness of each part of the tube blank. Explore the principle of material replenishment of the branch pipe. Combining the traditional internal high-pressure forming technology of tees with the newly designed mobile die forming technology, a new forming process for the branch pipe of the tee is designed, and the double-side mobile branch pipe forming process is explored according to the displacement variables and internal pressure variables. In the study of hydroforming, Jun Young Park and Sang Wook Han from Pusan National University, South Korea, proposed an advanced sealing system composed of a die spring, a cylindrical sleeve and an end punch, as shown in Figures 1-3. This sealing system prevents hydraulic leakages and ensures the internal forming pressure by increasing the contact between the axial force of the punch and the reaction force generated by the punch.
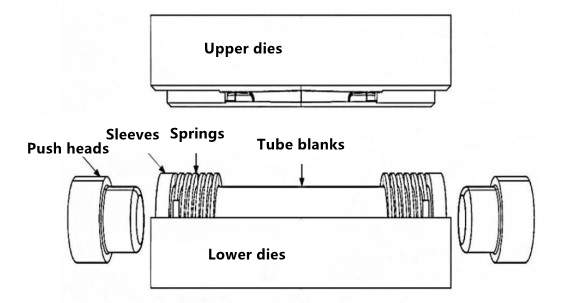
Figure 1-3 Sealing system dies
T. Nakamori, K. Shukuno and others from Tokyo Metropolitan University in Japan put sensors in the mold cavity of the original hydroforming control system in order to improve the shape accuracy of the Y-shaped tube protrusion. The shape accuracy and dimensional accuracy of the bulging top of the formed part are relatively high. C. Nikhare, M. Weiss and others used the principle of plastic energy to estimate the minimum pressure required for low-pressure hydroforming of parts, and established a corresponding model. The modified model showed that the minimum pressure required depends on the yield stress of the pipe material, the thickness of the tube material and the straight length of the tube section in contact with the die; through a sensitivity analysis, it was determined that the required pressure is greatly influenced by the yield stress of the tube. S.E. Eftekhari Shahria, S.Y. Ahmadi Boroughanib and others used ultrasonic vibration to improve the contact conditions between the pipe and the mold cavity boundary, and solved the established analytical model through the wall thickness and the hydroformed pipe radius in order to prove that the vibration affects the wall thickness and angle. Superimposing ultrasonic vibration with the process can significantly improve the corner filling rate of the tube wall and make the tube wall thickness more uniform. Verena Psyk, Thomas Lieber and others applied finite element simulations to characterize and quantify these loads. The microstructure of the joint was analyzed in the electromagnetic connection process, and the performance of the joint was evaluated by an experimental model.
In essence, the reducing tee also follows the forming process of the tee, so it has the same process characteristics. With the rapid development of the pipe bulging process, according to the different needs of users, the methods used in the pipe bulging process are also different. According to different bulging media, several bulging methods are briefly introduced. The extrusion medium is bulging, and the pressure is increased by adding a medium to the inside of the pipe to increase the internal pressure. Extrusion is a method in which the punches at both ends pressurize the medium in the cavity in a closed environment. Extrusion medium bulging is divided into rigid extrusion media, fluid extrusion media, plastic extrusion media and elastic extrusion media. The viscous medium is bulging, and the pressure in the forward and reverse directions is controlled by operating the viscous medium in the pressure control cylinder and the reverse viscous medium pressure cylinder, so that the pressure generated in different areas of the blank is different to control the blank and the cavity filming, and finally obtain the desired of forming parts. This medium does not require high requirements for sealing like hydraulic bulging. The new bulging medium is bulging, which will consist of lead (Pb), tin (Sn), bismuth (Bi) and other low melting point metals in different proportions, and low melting point alloys with different melting points, different hardness and different freezing points can be obtained. The use of this low melting point alloy as a new process, new technology and new material for tube bulging has been widely recognized as a relatively reasonable, fast, simple and low-cost bulging medium.
After decades of technological development, some experts and scholars at home and abroad have slightly improved the forming of tees, for example, pipe fittings formed by high pressure in a hot state. First, heat the mold to the specified temperature, then put the tube blank in the cavity to preheat; inject the hot medium into the pipe. When the pipe reaches the set temperature, start to apply pressure and axial feed to form the tube close to the inner cavity of the mold, forming a hollow variable cross-section part. Jianchun He and Xiaoting Xiao and others from the Guangdong University of Technology used the ABAQUS explicit algorithm to simulate the tee, and used the influence of the axial displacement variable and internal pressure variable on the height, maximum and minimum wall thickness of the formed branch pipe, and analyzed the distribution of wall thickness of each part of the tube blank. Explore the principle of material replenishment of the branch pipe. Combining the traditional internal high-pressure forming technology of tees with the newly designed mobile die forming technology, a new forming process for the branch pipe of the tee is designed, and the double-side mobile branch pipe forming process is explored according to the displacement variables and internal pressure variables. In the study of hydroforming, Jun Young Park and Sang Wook Han from Pusan National University, South Korea, proposed an advanced sealing system composed of a die spring, a cylindrical sleeve and an end punch, as shown in Figures 1-3. This sealing system prevents hydraulic leakages and ensures the internal forming pressure by increasing the contact between the axial force of the punch and the reaction force generated by the punch.

Figure 1-3 Sealing system dies
T. Nakamori, K. Shukuno and others from Tokyo Metropolitan University in Japan put sensors in the mold cavity of the original hydroforming control system in order to improve the shape accuracy of the Y-shaped tube protrusion. The shape accuracy and dimensional accuracy of the bulging top of the formed part are relatively high. C. Nikhare, M. Weiss and others used the principle of plastic energy to estimate the minimum pressure required for low-pressure hydroforming of parts, and established a corresponding model. The modified model showed that the minimum pressure required depends on the yield stress of the pipe material, the thickness of the tube material and the straight length of the tube section in contact with the die; through a sensitivity analysis, it was determined that the required pressure is greatly influenced by the yield stress of the tube. S.E. Eftekhari Shahria, S.Y. Ahmadi Boroughanib and others used ultrasonic vibration to improve the contact conditions between the pipe and the mold cavity boundary, and solved the established analytical model through the wall thickness and the hydroformed pipe radius in order to prove that the vibration affects the wall thickness and angle. Superimposing ultrasonic vibration with the process can significantly improve the corner filling rate of the tube wall and make the tube wall thickness more uniform. Verena Psyk, Thomas Lieber and others applied finite element simulations to characterize and quantify these loads. The microstructure of the joint was analyzed in the electromagnetic connection process, and the performance of the joint was evaluated by an experimental model.
In essence, the reducing tee also follows the forming process of the tee, so it has the same process characteristics. With the rapid development of the pipe bulging process, according to the different needs of users, the methods used in the pipe bulging process are also different. According to different bulging media, several bulging methods are briefly introduced. The extrusion medium is bulging, and the pressure is increased by adding a medium to the inside of the pipe to increase the internal pressure. Extrusion is a method in which the punches at both ends pressurize the medium in the cavity in a closed environment. Extrusion medium bulging is divided into rigid extrusion media, fluid extrusion media, plastic extrusion media and elastic extrusion media. The viscous medium is bulging, and the pressure in the forward and reverse directions is controlled by operating the viscous medium in the pressure control cylinder and the reverse viscous medium pressure cylinder, so that the pressure generated in different areas of the blank is different to control the blank and the cavity filming, and finally obtain the desired of forming parts. This medium does not require high requirements for sealing like hydraulic bulging. The new bulging medium is bulging, which will consist of lead (Pb), tin (Sn), bismuth (Bi) and other low melting point metals in different proportions, and low melting point alloys with different melting points, different hardness and different freezing points can be obtained. The use of this low melting point alloy as a new process, new technology and new material for tube bulging has been widely recognized as a relatively reasonable, fast, simple and low-cost bulging medium.
Post URL: https://www.landeepipefitting.com/forming-processes-and-methods-of-tees.html
Landee is a professional industrial pipe fitting manufacturer and be well accepted by customers all over the world, we has been producing Pipe Fitting for a variety of applications since 1985. welcome to access our website: https://www.landeepipefitting.com.
Previous: How to Find the Lowest & Highest Points of Eccentric Reducers?
Next: Feasibility of High-pressure Forming in Reducing Tees
Next: Feasibility of High-pressure Forming in Reducing Tees
