Leakages of Pipe Caps of Hot-wall Tubes of Hydrogen Conversion Furnaces (Part One)
Posted: 07/29/2021 10:03:43 Hits: 17
Abstract: During the operation of the hydrogen manufacturing conversion furnace, the furnace tube and hot-wall tube of the hydrogen manufacturing furnace work at high temperatures, and the medium in the tube is complicated. Cracks are found in the cap of the hot-wall tube during the operation. Research and analysis on the leakage of the hot-wall pipe cap of the hydrogen manufacturing furnace are conducted in this article. Rectification suggestions are put forward to ensure the long-term and stable operation of the device.
1. The overview of the failure
In November 2017, the cover plate of the insulation box was opened after the furnace was shut down. It was found that the welding seam of the hot-wall tube cap at the lower part of the furnace tube cracked. The material information of the cap and process media is shown in Table 1.
Table 1 The material information of the cap and process media
1. The overview of the failure
In November 2017, the cover plate of the insulation box was opened after the furnace was shut down. It was found that the welding seam of the hot-wall tube cap at the lower part of the furnace tube cracked. The material information of the cap and process media is shown in Table 1.
Table 1 The material information of the cap and process media
| Materials | ZG12Ni32Cr20Nb |
| Specifications | ID160 x 28MSW x 56MSW |
| Casting methods | Static casting |
| Operating pressure | 2.6 to 2.7MPa |
| Operating temperature | 770°C |
| Internal media | H2, CH4, CO, steam, etc. |
| External media | Air and smoke |
2. The content and results of the failure analysis
2.1 The macro inspection
The inner wall of the cap is black and the surface is relatively smooth. There was a circular welding seam in the middle of the straight side section, and a circular crack parallel to the welding seam at the bottom rounded corner. The crack has a shape of crescent. Judging from the shape, it started from the part where there was the biggest crack and then expanded to both sides; longitudinal cracks perpendicular to the main crack were generated. After the crack was intercepted and observed, it was found that the crack expanded in a "Z" shape along a 45° angle in the wall thickness direction. There was a large area of defect in the corresponding part of the outer wall of the cap and the inner wall of the crack. Obvious traces of metal melting could be seen in the defected part. A circular crack and a branch crack perpendicular to the circular crack reaching the sampling section could be seen in the part parallel to the circular welding seam. The overall crack is relatively straight. From the cross-section of the crack, it could be seen that the weld reinforcement is relatively great. The crack started from the outer surface, and the propagation direction was close to the fusion line of the welding seam; the crack expanded straight in the wall thickness direction.
2.2 The analysis of the sampling and processing
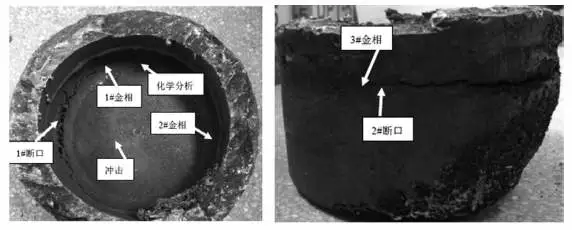
The failure of the pipe cap was cracking. The failure existed in the two parts: one was the rounded corner of the inner wall, and the other was the part between the outer wall and the circular welding seam. Therefore, the two parts were mainly sampled for analysis. The sampling position is shown in figure 1.
2.3 The analysis of the chemical composition
According to GB/T11170-2008 and GB/T20123-2006, The analysis of the chemical composition is performed, and the results are shown in Table 2.
2.4 Metallographic analysis
According to the regulations of GB/T13298, the sample was mechanically polished and corroded by ferric chloride hydrochloric acid aqueous solution. The backscattered electron image and secondary electron image of the sample were collected by the scanning electron microscope, and the EDS line of the precipitated phase of the grain boundary was scanned and analyzed. Observation and analysis of the phase composition in the metal structure were conducted. The corresponding metallographic structure was austenite plus metal carbide.
Table 2 The analysis of the chemical composition
| Elements | C | S | P | Si | Mn |
| Test values | 0.19 | 0.007 | 0.017 | 0.72 | 0.84 |
| Standard values | 0.08 to 0.16 | Less than and equal to 0.03 | Less than and equal to 0.03 | Less than and equal to 1.5 | Less than and equal to 1.25 |
| Elements | Cr | Ni | Mo | Nb | |
| Test values | 20.95 | 32.44 | Less than 0.060 | 1.08 | |
| Standard values | 19.0 to 22.0 | 31.0 to 34.0 | Less than and equal to 0.50 | 1.0 to 2.0 |
2.5 The analysis of mechanical properties
The impact test wass carried out in accordance with the requirements of GB/T229, and the results were shown in Table 3.
Table 3 The results of the analysis of mechanical properties
| The impact test | The size of the sample/mm | Test temperature/°C | Samples | The absorption energy of the impact kV2/J |
| 10 x 10 x 55 | 20 | Vertical directions | 25.0/11.5/10.5 |
2.6 The analysis of hardness
According to the provisions of GB/T4340.1, the hardness of the base material, welding seam and area near the crack of the sample was measured. The results were shown in Table 4.
Table 4 The analysis of hardness
| The inspecting part | Hardness values/HV10 | Average values | |
| Test values | Welding seams | 143.3/144.7/143.8 | 143.2 |
| Base materials | 166.5/169.0/167.2 | 167.5 | |
| Areas near the crack | 166.5/151.4/168.3 | 162 | |
Post URL: https://www.landeepipefitting.com/leakages-of-pipe-caps-of-hot-wall-tubes-of-hydrogen-conversion-furnaces-part-one.html
Landee is a professional industrial pipe fitting manufacturer and be well accepted by customers all over the world, we has been producing Pipe Fitting for a variety of applications since 1985. welcome to access our website: https://www.landeepipefitting.com.
Previous: The Analysis of Cracks in High-pressure Bends
Next: Leakages of Pipe Caps of Hot-wall Tubes of Hydrogen Conversion Furnaces (Part Two)
Next: Leakages of Pipe Caps of Hot-wall Tubes of Hydrogen Conversion Furnaces (Part Two)
