Performance Tests of Tees, Elbows and Reducers
Posted: 06/05/2024 10:39:53 Hits: 17
6. Machining, surfacing and product inspection
According to the product size drawings and the marking process card, the branch pipe center, main pipe center, branch pipe height, and product length are clarified. The cutting size and groove processing allowance are calculated, and the cutting and sizing machining are performed.
After the initial sizing process is completed, sandblasting and rust removal are performed, and subsequent internal surfacing is carried out. The surfacing equipment is vertical surfacing equipment. Because the tee has an irregular shape, the fusion between the surfacing welds is given special attention. After the surfacing is completed, subsequent groove processing, sizing processing, dimensional inspection, non-destructive inspection, pickling, marking and other subsequent processes are carried out.
7. Mechanical performance tests of the product
After the initial sizing process is completed, sandblasting and rust removal are performed, and subsequent internal surfacing is carried out. The surfacing equipment is vertical surfacing equipment. Because the tee has an irregular shape, the fusion between the surfacing welds is given special attention. After the surfacing is completed, subsequent groove processing, sizing processing, dimensional inspection, non-destructive inspection, pickling, marking and other subsequent processes are carried out.
7. Mechanical performance tests of the product
The offshore oil and gas field production system has very high requirements for the reliability of underwater forging products, including toughness indicators such as low-temperature impact, as well as upper limits for yield and tensile strength values. Using the 8-inch elbow as an example, the test data analysis from the mechanical performance test is as follows.
7.1 Tensile properties
Tensile tests measure various strength and plasticity properties of materials. Strength usually refers to the ability of materials to resist elastic deformation, plastic deformation, and fracture under external forces. The tensile properties of elbows are shown in Table 3.
Table 3 Tensile properties of elbows
7.1 Tensile properties
Tensile tests measure various strength and plasticity properties of materials. Strength usually refers to the ability of materials to resist elastic deformation, plastic deformation, and fracture under external forces. The tensile properties of elbows are shown in Table 3.
Table 3 Tensile properties of elbows
| Items | Tensile strength | Yield strength | Elongation |
| Raw materials | 608Mpa | 503Mpa | 30% |
| Elbows | 625Mpa | 510Mpa | 29% |
Comparing the performance data of raw materials (forged pipes) and elbows shows that their tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation meet the requirements through the hot pressing process and re-tempering heat treatment.
7.2 Impact properties
Impact properties are used to evaluate the impact resistance or judge the brittleness and toughness of materials, also known as impact toughness. The impact properties of elbows are shown in Table 4, and their values meet the standard requirements.
Table 4 Impact properties of elbows
| Items | Impact energy-1 | Impact energy-2 | Impact energy-3 |
| Raw materials | 215J | 258J | 257J |
| Elbows | 310J | 307J | 296J |
7.3 Grain sizes
The grain size of the forged pipe’s raw material is 8.0, and the grain size of elbows after hot pressing and re-tempering heat treatment is 10.5. The grain size reflects the size obtained during the actual heat treatment of the steel part or under hot working conditions, which directly affects the structure and performance of the product obtained after the steel is cooled. The grain size of the product can be refined using appropriate heat treatment parameters.
Figure 6 Metallographic photo of the elbow’s cladding layer
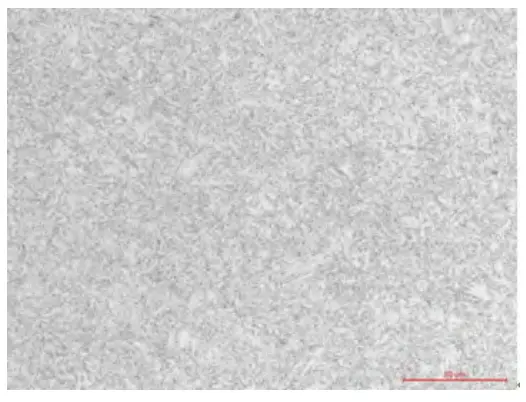
7.4 Pitting detection data
After the inner wall of the elbow is clad, FeCl3 pitting detection is performed to detect the pitting corrosion resistance of the product. The detection is performed according to ASTM G48, Method A. The number of samples is 3. The temperature of the FeCl3 test solution is 50℃ and the immersion period is 72 hours. The calculation formula of the corrosion rate is as follows:
Corrosion rate (g/m2) = W/A
Wherein, A is the total sample area and W weight loss.
The pitting test data of the surfacing elbow is Table 5.
Table 5 Pitting detection data
| Items | Corrosion rate (g/m2) | Average value (g/m2) |
| Sample 1 | 0.0741 | 0.0617 |
| Sample 2 | 0.0741 | |
| Sample 3 | 0.0370 |
The analysis of the pitting detection data shows that the Inconel 625 cladding layer has excellent corrosion resistance (the test pass standard is 4g/m²)
8. Conclusion
Pipe fittings such as tees, elbows, and reducers are widely used in underwater production facilities, and play a role in changing the direction, diversion, and diameter of oil and gas transmission. Changes in oil and gas flow and speed often cause stress concentration and fatigue on pipe fittings, imposing strict requirements on their strength and corrosion resistance. Tees, elbows, and reducers formed by mud pressing and hot pressing processes using A694 F65 forged pipes as raw materials have excellent mechanical properties after heat treatment and tempering. After the inner wall is clad with Inconel 625 cladding layer, it has good corrosion resistance.
Post URL: https://www.landeepipefitting.com/performance-tests-of-tees-elbows-and-reducers.html
Landee is a professional industrial pipe fitting manufacturer and be well accepted by customers all over the world, we has been producing Pipe Fitting for a variety of applications since 1985. welcome to access our website: https://www.landeepipefitting.com.
Previous: Production of Elbows and Reducers for Underwater Oil & Gas
Next: Bends Used for Boiler Tubes
Next: Bends Used for Boiler Tubes

