Understanding Expansion Joints in Pipelines
Posted: 04/01/2024 04:22:33 Hits: 41
Expansion joints, also known as bellows or compensators, are vital components in pipelines. They consist of bellows, end pipes, supports, flanges, and other accessories. By harnessing the expansion and contraction of the bellows, they absorb variations in pipeline dimensions caused by factors like thermal changes, while also dampening vibrations and noise. In the following, we will discuss their functions, classification, and installation considerations to help you choose the right expansion joints for your needs.
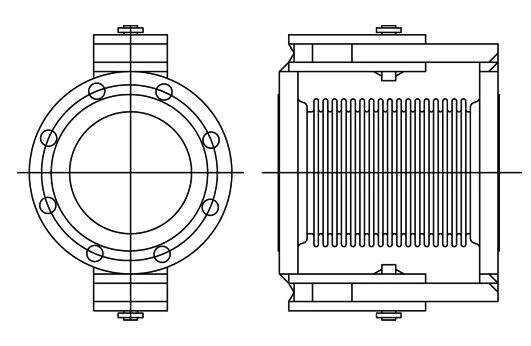
Functions and Purposes
Expansion joints primarily serve to ensure the safe operation of pipelines, with the following functions:
Compensating for Pipeline Deformations: They absorb axial, lateral, and angular thermal deformations of pipelines, thereby preventing stress concentrations and potential ruptures.
Facilitating Expansion and Contraction: The expansion and contraction capabilities of expansion joints allow for easier installation and disassembly of valves and pipeline sections, enhancing operational efficiency.
Vibration Dampening: By absorbing equipment vibrations, expansion joints reduce the adverse effects of vibrations on pipelines and associated equipment, extending their service life.
Resisting External Forces: They absorb deformations caused by external forces such as earthquakes and ground subsidence, enhancing the pipeline's resilience to disasters.
Facilitating Expansion and Contraction: The expansion and contraction capabilities of expansion joints allow for easier installation and disassembly of valves and pipeline sections, enhancing operational efficiency.
Vibration Dampening: By absorbing equipment vibrations, expansion joints reduce the adverse effects of vibrations on pipelines and associated equipment, extending their service life.
Resisting External Forces: They absorb deformations caused by external forces such as earthquakes and ground subsidence, enhancing the pipeline's resilience to disasters.
Classification
Expansion joints can be categorized based on their functionality and structural characteristics:
Axial Expansion Joints: Internal Pressure, External Pressure, Compound, Unrestrained, and Buried expansion joints.
Lateral Expansion Joints: Large Tie Rod and Small Tie Rod lateral expansion joints.
Angular Expansion Joints: Single Hinged, Universal Hinged, and Compound Hinged expansion joints.
Pressure Balanced Expansion Joints: Straight Pipe Pressure Balanced, Bending Pipe Pressure Balanced, and Internal-External Pressure Balanced expansion joints.
Lateral Expansion Joints: Large Tie Rod and Small Tie Rod lateral expansion joints.
Angular Expansion Joints: Single Hinged, Universal Hinged, and Compound Hinged expansion joints.
Pressure Balanced Expansion Joints: Straight Pipe Pressure Balanced, Bending Pipe Pressure Balanced, and Internal-External Pressure Balanced expansion joints.
Installation Considerations
During the installation of expansion joints, the following factors should be taken into consideration.
1. Verification of Model and Specifications: Ensure that the expansion joint's model and specifications meet the design requirements, ensuring compatibility with the pipeline.
2. Orientation of Flow Directors: Align the flow direction of the internal sleeve of the expansion joint with the direction of fluid flow to ensure smooth fluid passage.
3. Avoidance of Adjustment Errors: Refrain from using the expansion joint's deformation to adjust installation errors in pipelines to prevent compromising its functionality.
4. Protective Measures: Prevent welding slag from splashing onto the surface of the bellows during installation and avoid mechanical damage to the bellows by employing protective measures.
5. Reinforcement of Fixation: Reinforce the secondary fixed pipe rack at the end of the pipe section containing the expansion joint during pressure testing to prevent pipe movement or rotation. After hydrostatic testing, promptly drain any accumulated water from the bellows and dry the surface to prevent corrosion and damage.
2. Orientation of Flow Directors: Align the flow direction of the internal sleeve of the expansion joint with the direction of fluid flow to ensure smooth fluid passage.
3. Avoidance of Adjustment Errors: Refrain from using the expansion joint's deformation to adjust installation errors in pipelines to prevent compromising its functionality.
4. Protective Measures: Prevent welding slag from splashing onto the surface of the bellows during installation and avoid mechanical damage to the bellows by employing protective measures.
5. Reinforcement of Fixation: Reinforce the secondary fixed pipe rack at the end of the pipe section containing the expansion joint during pressure testing to prevent pipe movement or rotation. After hydrostatic testing, promptly drain any accumulated water from the bellows and dry the surface to prevent corrosion and damage.
The correct selection and installation of expansion joints are crucial for the stable operation of pipeline systems. By understanding their classification, functions, and installation considerations, you can accurately choose suitable expansion joints and ensure their proper installation, effectively safeguarding the safe and stable operation of your pipeline system, and ensuring smooth production processes.
Post URL: https://www.landeepipefitting.com/understanding-expansion-joints-in-pipelines.html
Landee is a professional industrial pipe fitting manufacturer and be well accepted by customers all over the world, we has been producing Pipe Fitting for a variety of applications since 1985. welcome to access our website: https://www.landeepipefitting.com.
Previous: Key Functions of Barred Tees in Pipeline Systems
Next: Stainless Steel Stub Ends for Waterproofing
Next: Stainless Steel Stub Ends for Waterproofing
